

Use the "Generalization" tool to link one use case with another.The use cases will now be linked by an arrow with a triangular head.The generalisation relationship arrow should point from the more specific use case to the more general use case.ĬLASS DIAGRAMClass, Attribute, OperationSelect "Class" on the Violet sidebar and place the symbol.In the Class's properties fill out the name, attributes and methods(operations).Class names consist of a lowercase noun or nouns. The text is present above the line.The extend relationship's arrow symbol should point from one use case (B) to another (A), where use case B represents an extension of the functionality of use case A. Use the "" tool to link one use case with another.The use cases will now be linked by a dotted line with an open arrow head.
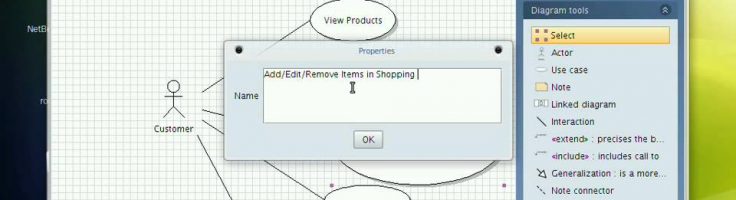
Use the "" tool to link one use case with another.The use cases will now be linked by an relationship symbol.The include relationship's arrow symbol should point from one use case (A) to another (B) that represents some subset of the functionality of use case A. Select "Use case" on the Violet sidebar and place the symbol.In the properties box of the use case, alter the name string to the desired value.Īssociation RelationshipUse the "Interaction" tool to link an actor to a use case.The actor and use case will now be linked by an association relationship symbol (a line).Include Relationship To prepare a new blank canvas, create a new use case diagramActorSelect "Actor" on the Violet sidebar and place the symbol.In the Actor's properties, alter the name string to the desired value. The properties box can again be brought up by right clicking on this line.Edit the fields to the desired values and click OK. the association symbol, when creating a class diagram).With the tool selected place the mouse cursor over the symbol to linkfrom.Hold down the left mouse button, drag the cursor over the symbol to linkto, and release.The symbols are now linked by the desired link (shown as some form of line graphic). To join two symbols with some kind of link:Select the desired link symbol on the sidebar (e.g. the class symbol, when creating a class diagram).Left click somewhere on the canvas to place a new symbol.Right click on the symbol to edit its properties.Edit the fields to the desired values and click OK. 6Placement of 'Node' EntitiesLeft click (select) the desired symbol on the Violet sidebar (e.g. Conceptually, these correspond to the nodes and edges (links) within graph theory.
Diagrams have symbols representing entities like classes, actors, use cases, etc and symbols representing relationships between these entities like associations, messages, etc. 2UML Diagram TypesUML diagrams can be assigned to two broad categories:structure diagrams and behavioural diagrams.Structure diagrams are staticconsider the relationship between the structural components of the system, without considering the system's behaviour over time.6 structure diagrams: class, component, composite structure, deployment, object, and package.3Behavioural diagrams are dynamic and consider processes and how the system functions over time.7 classes of behavioural diagram: activity, communication, interaction overview, sequence, state, timing, and use-case.4Violet UML supports the production of use-case, class, sequence, state, activity and object diagrams.5Drawing Diagrams With Violet UMLAll UML diagrams are, in a general sense, made up of symbols. Violet UML can function independently as a stand-alone application or as a plug-in for the Eclipse IDE Eclipse is a cross-platform, open source, integrated development environment). Violet UML Tool1OverviewViolet UML is an open source UML tool enables the easy creation of simple UML diagrams.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
